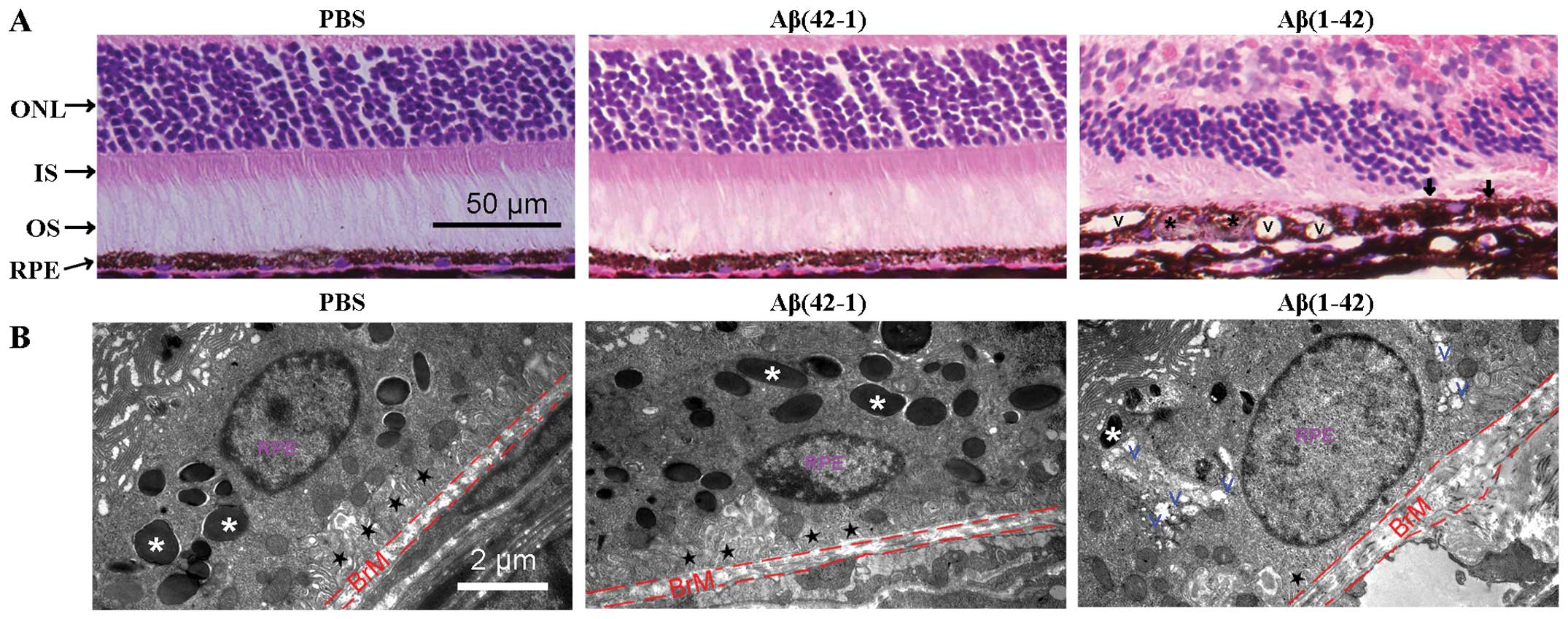
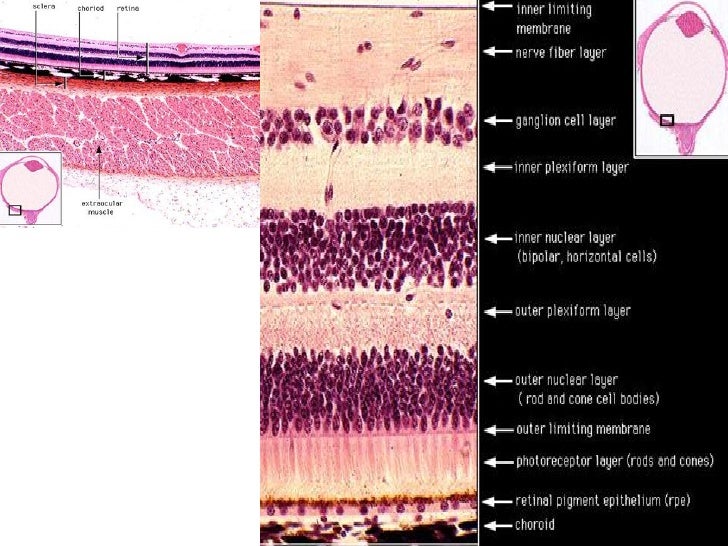
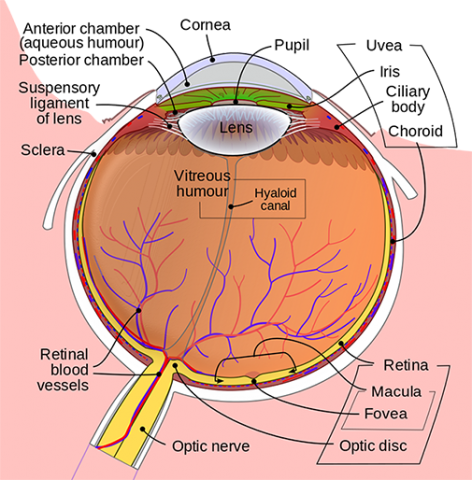
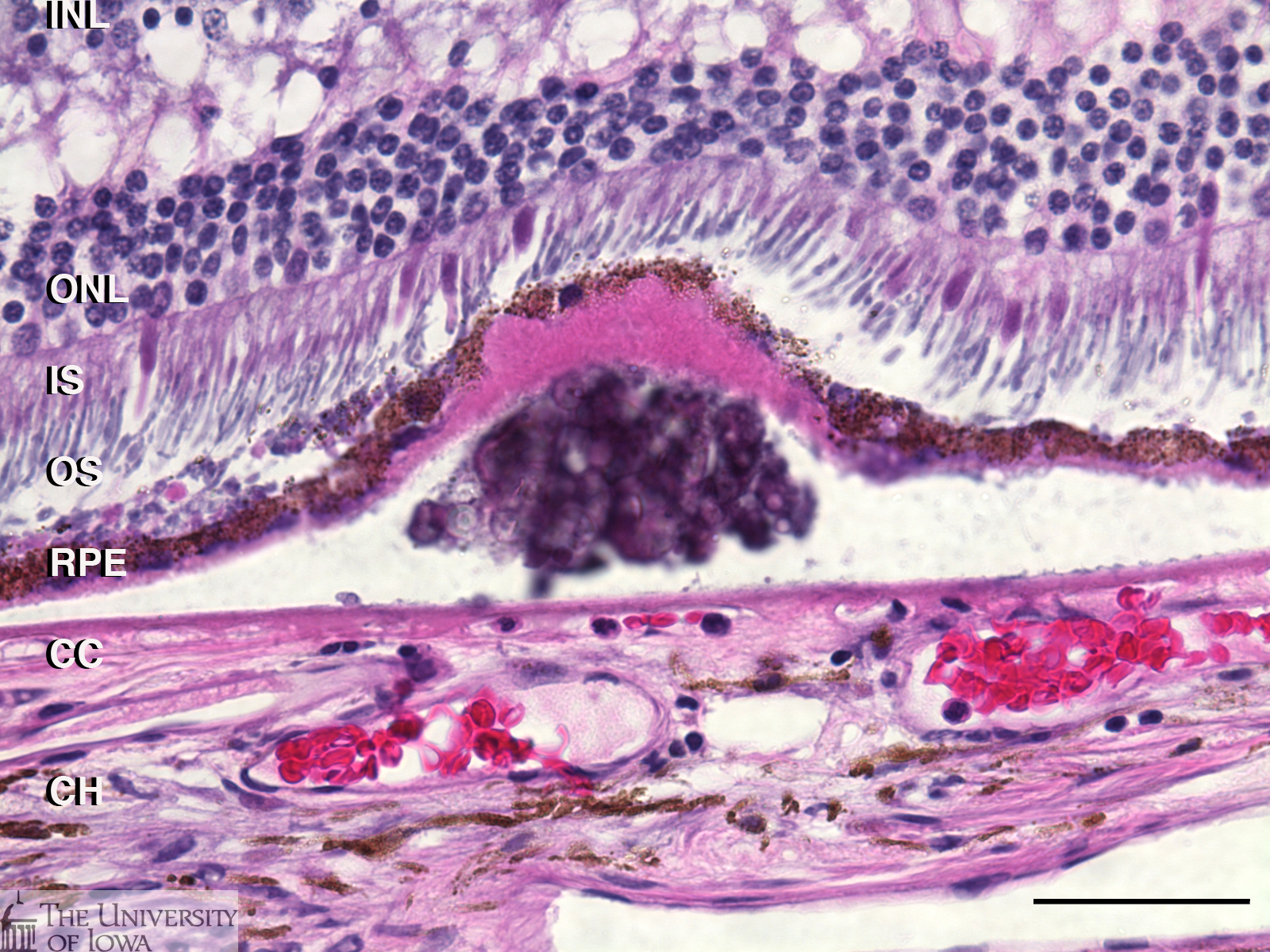
Retina Eye Histology
Relate retinal detachment to embryonic development.
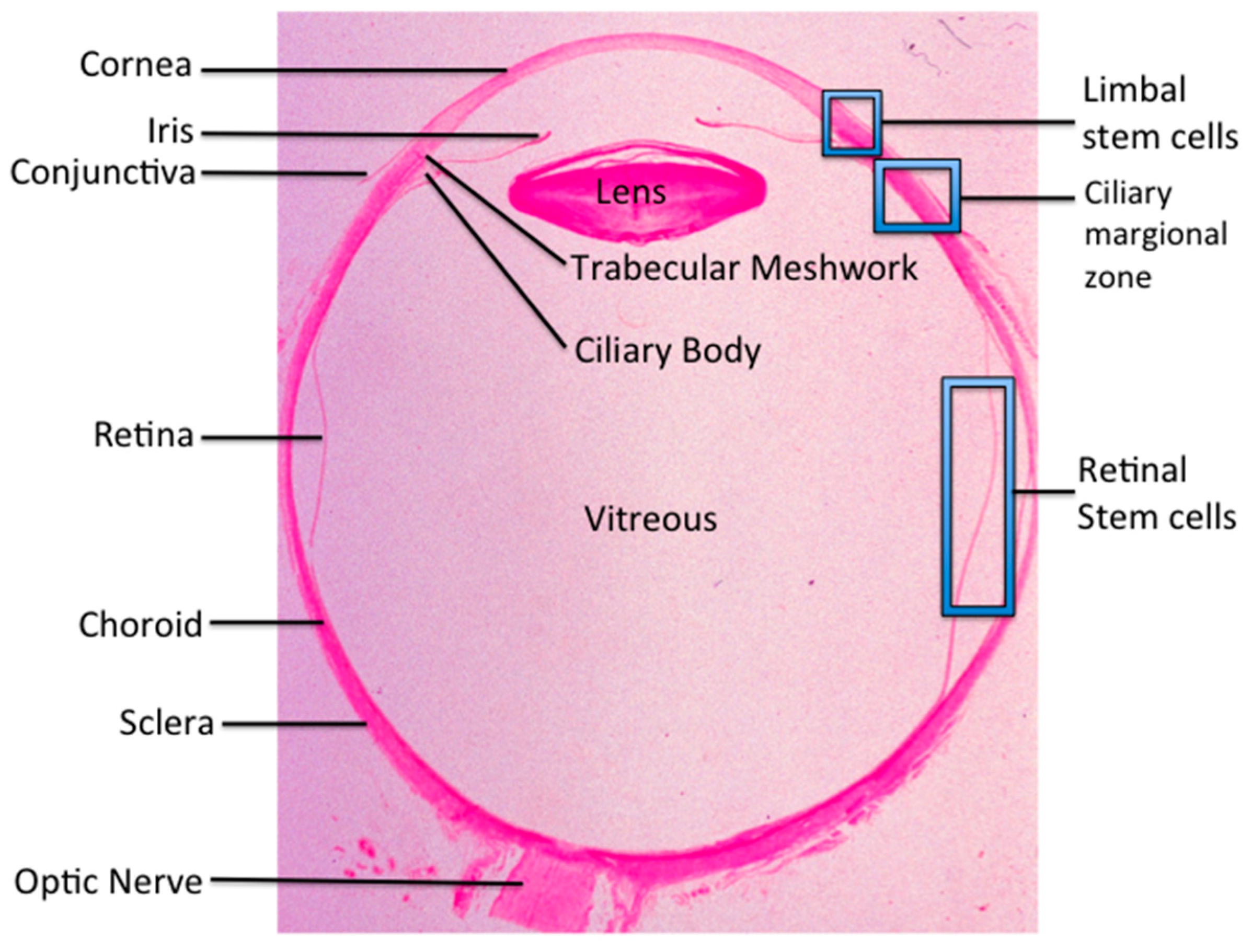
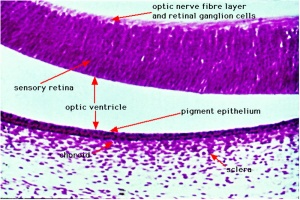
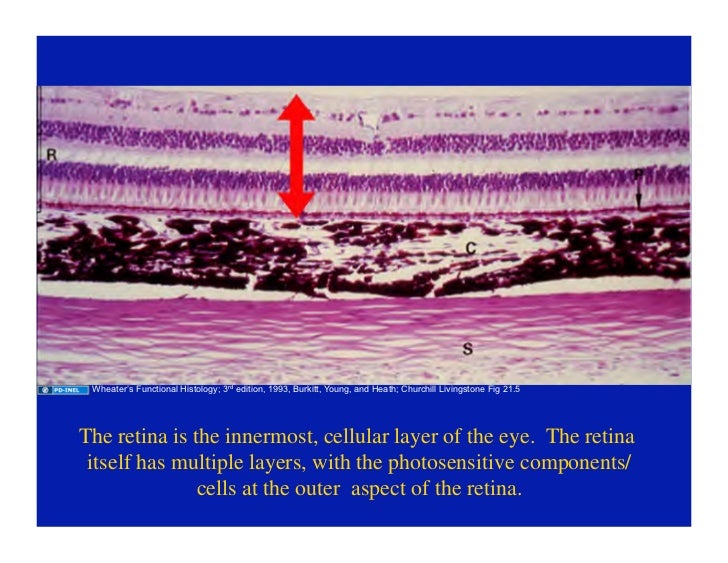
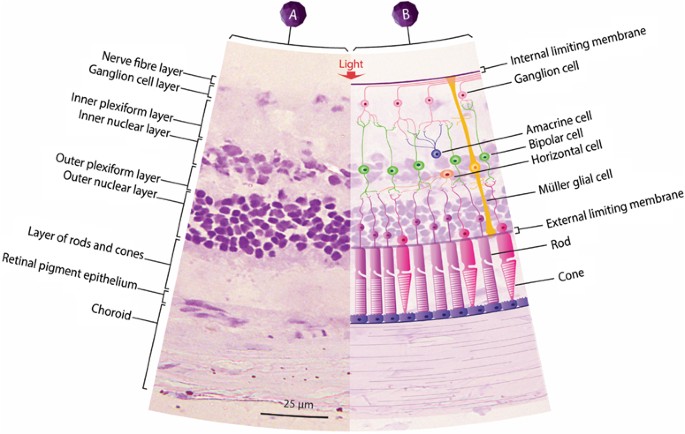
Retina eye histology. The following are commonly modalities of management for retinal disease. When an ophthalmologist uses an ophthalmoscope to look into your eye he sees the following view of the retina fig. Closest to the visual field and farthest from the brain is the axon terminal which releases a neurotransmitter called glutamate to bipolar cells. An understanding of the histology of the retina is essential to consider for complete insight into diseases involving a vital sensory component in the eye.
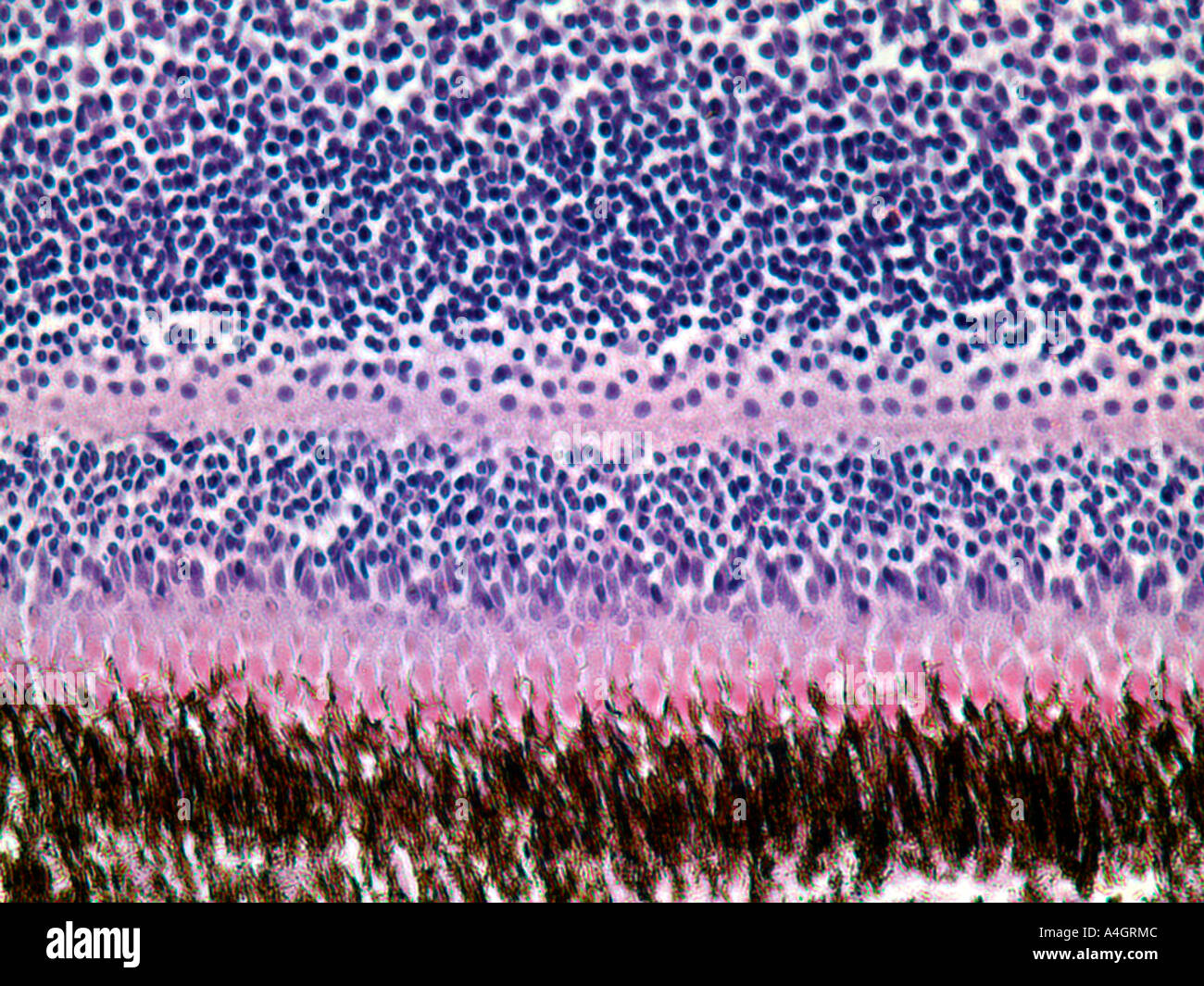
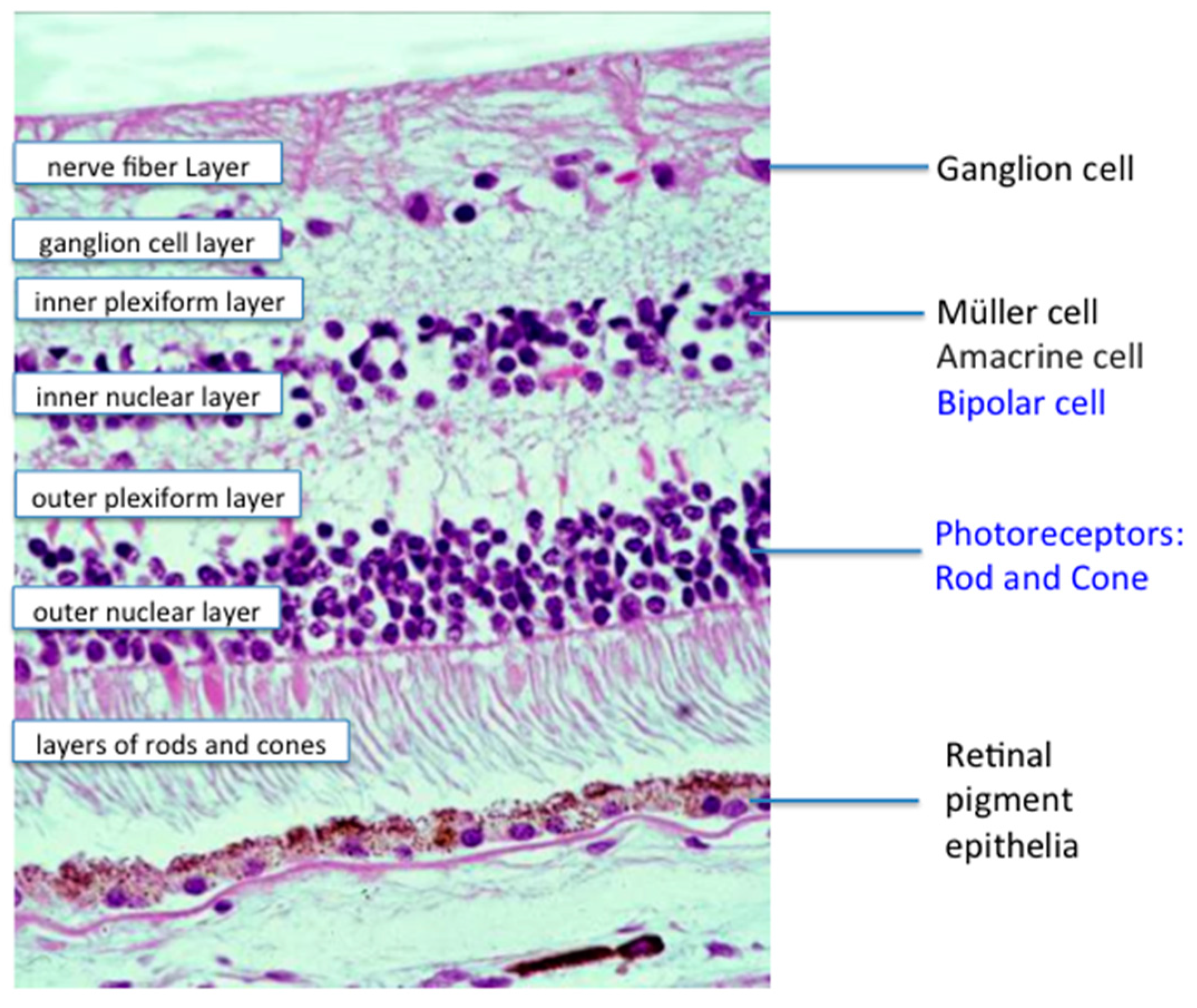
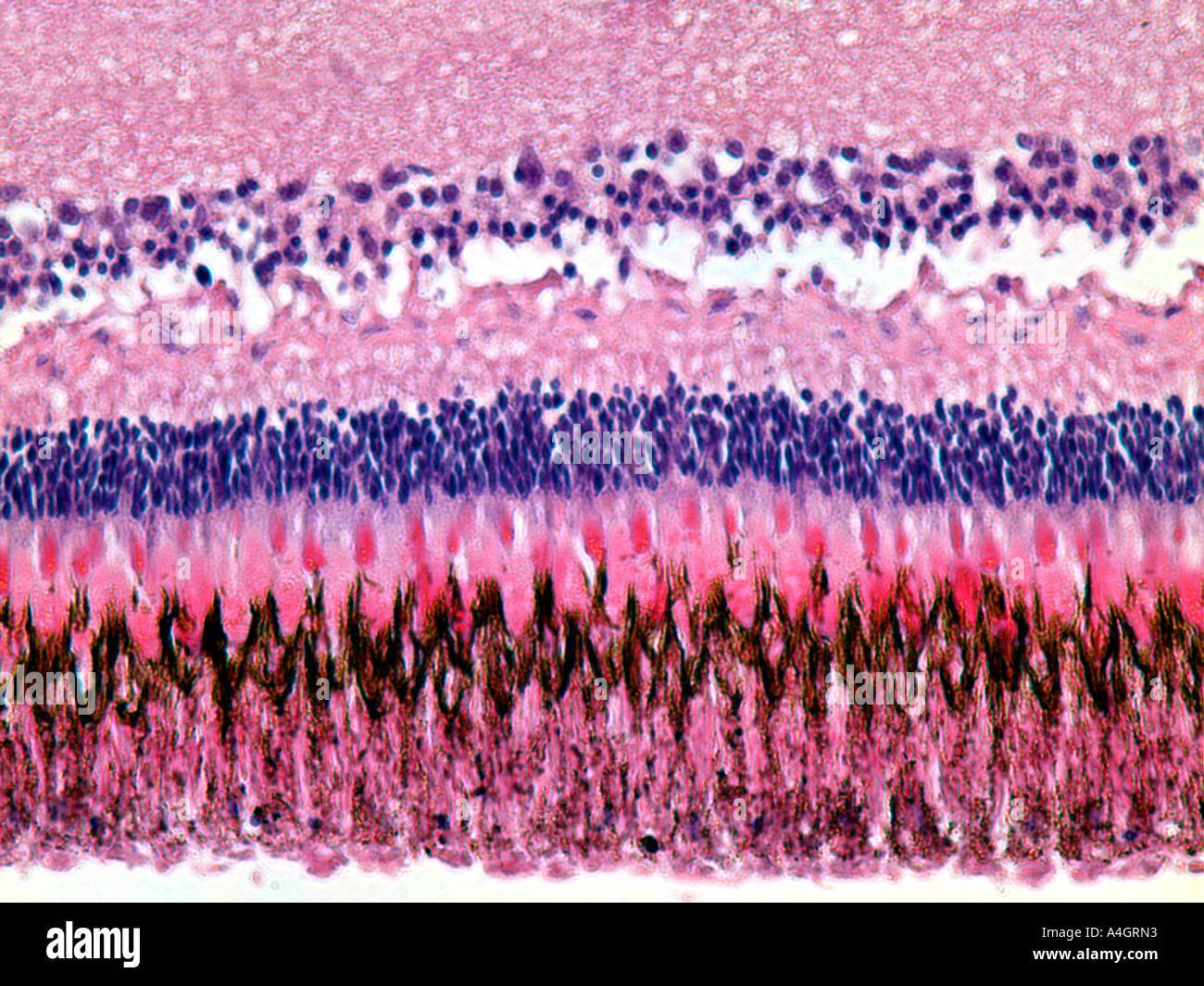
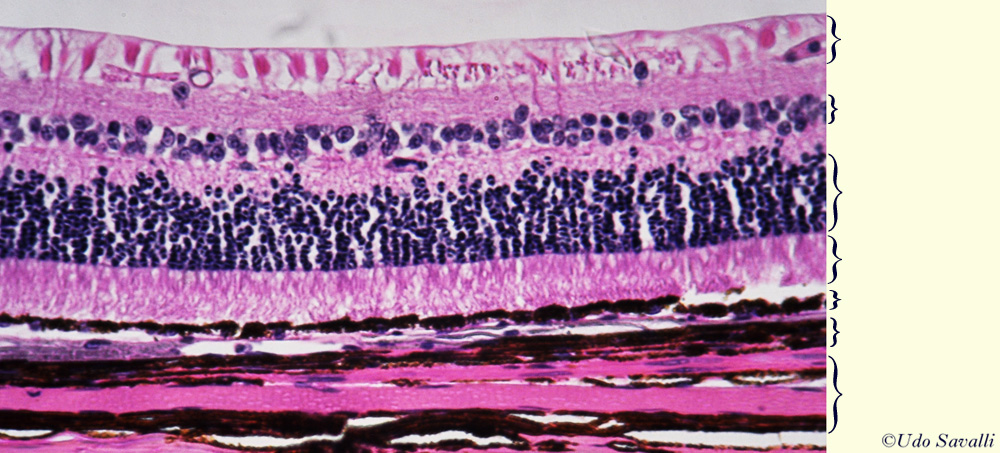
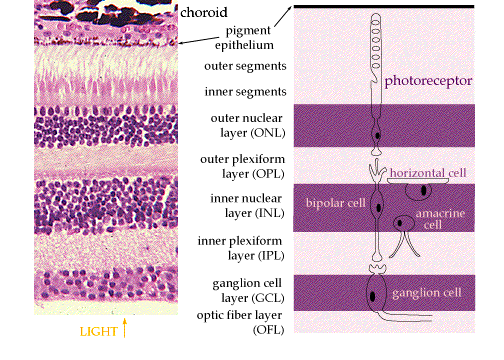
Rod and cone photoreceptors are found on the outermost layer of the retina. The octa image represents a projection of all retinal vascular plexuses. Histology retina statpearls ncbi bookshelf. Histology of the ear g 778a 778b.
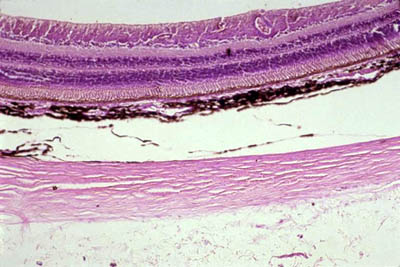
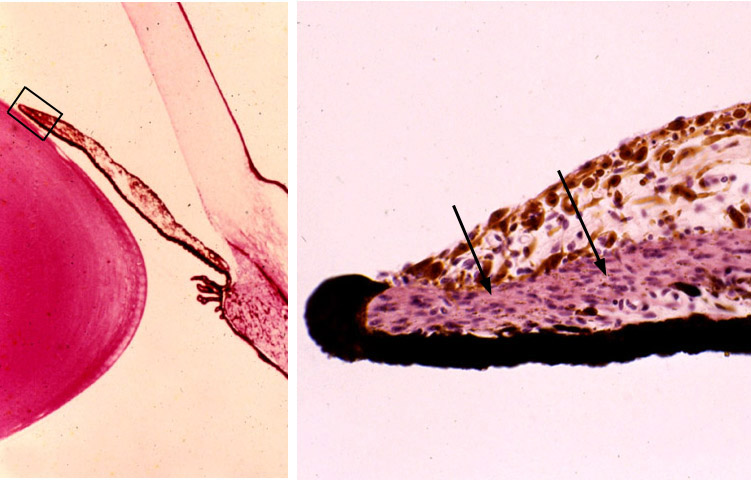
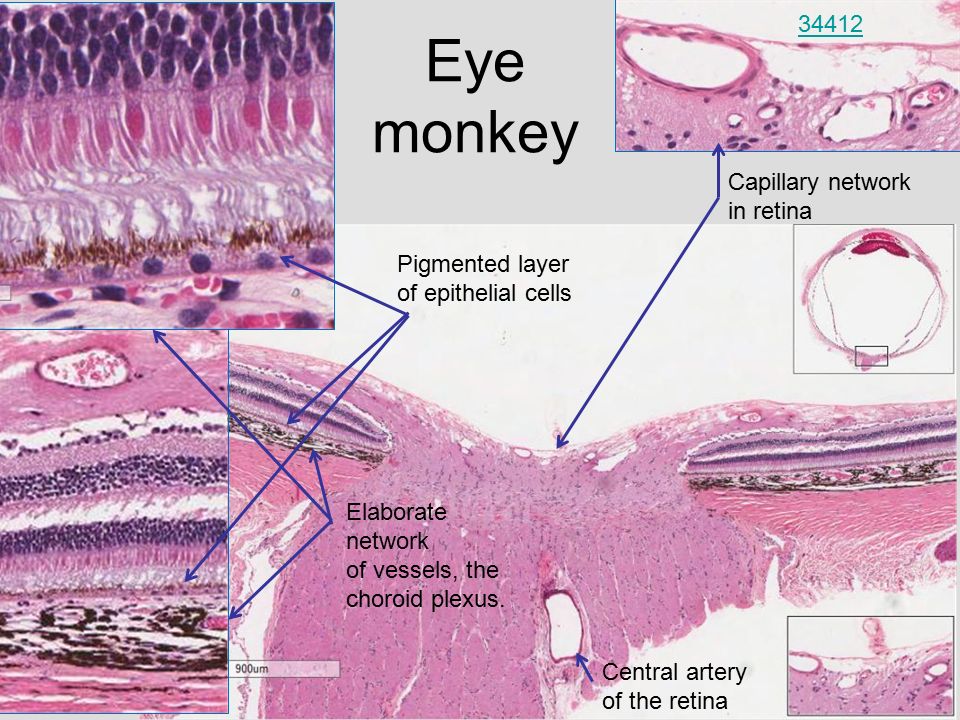
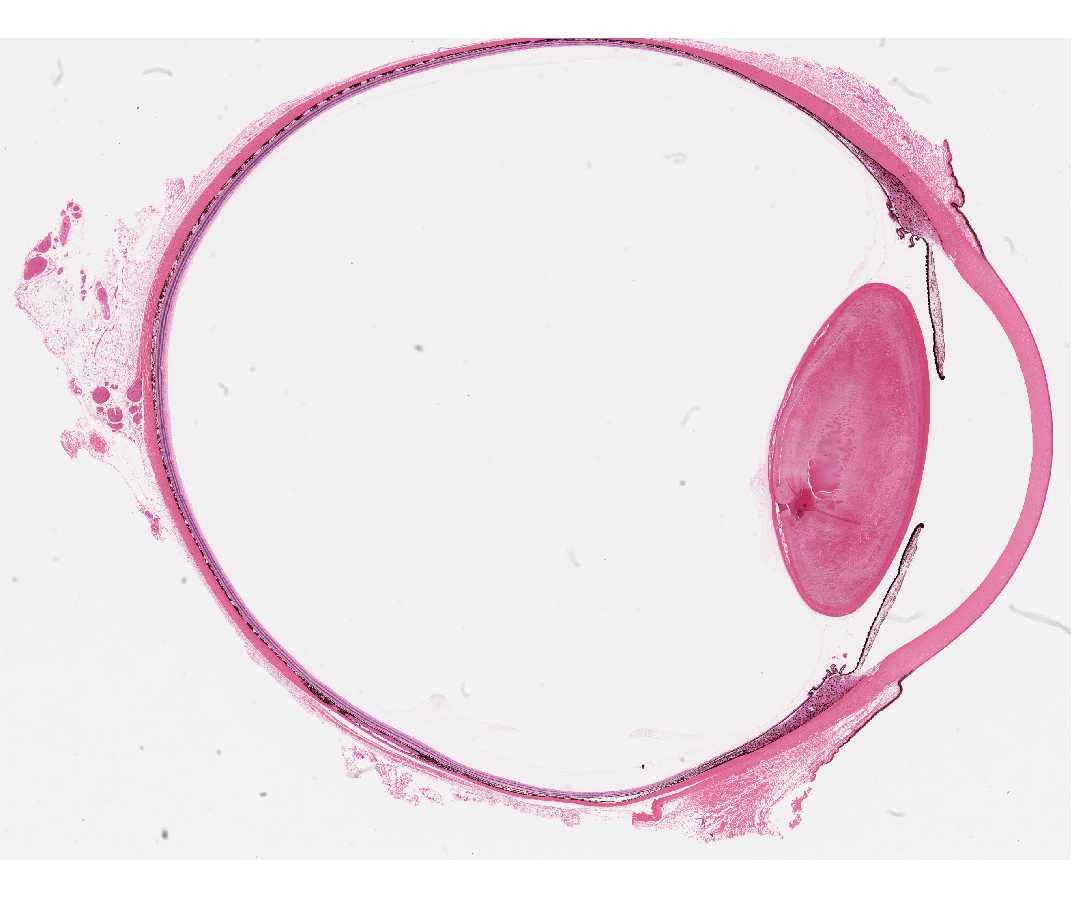
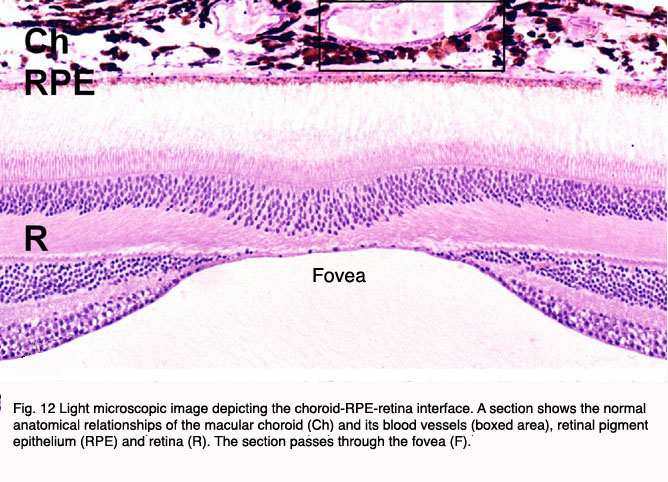
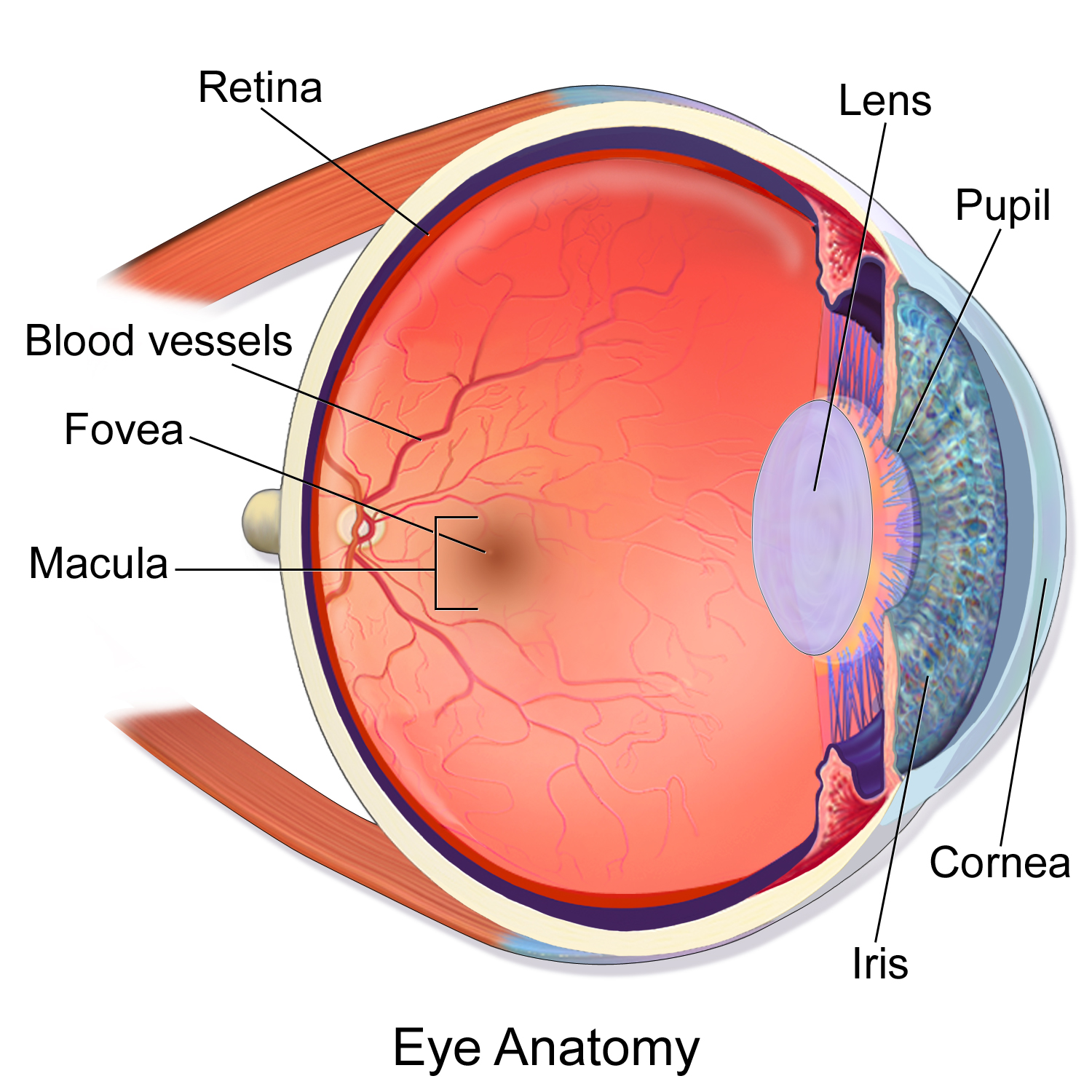
In the center of the retina is the optic nerve a circular to oval white area measuring about 2 x 15 mm across. It is in immediate contact with the vitreal cavity on one side and with the choroid of the uveal layer on the other side. The ciliary and iridial parts of the retina are described together with the ciliary process and iris. Reprinted with permission from balaratnasingam et al 2019.
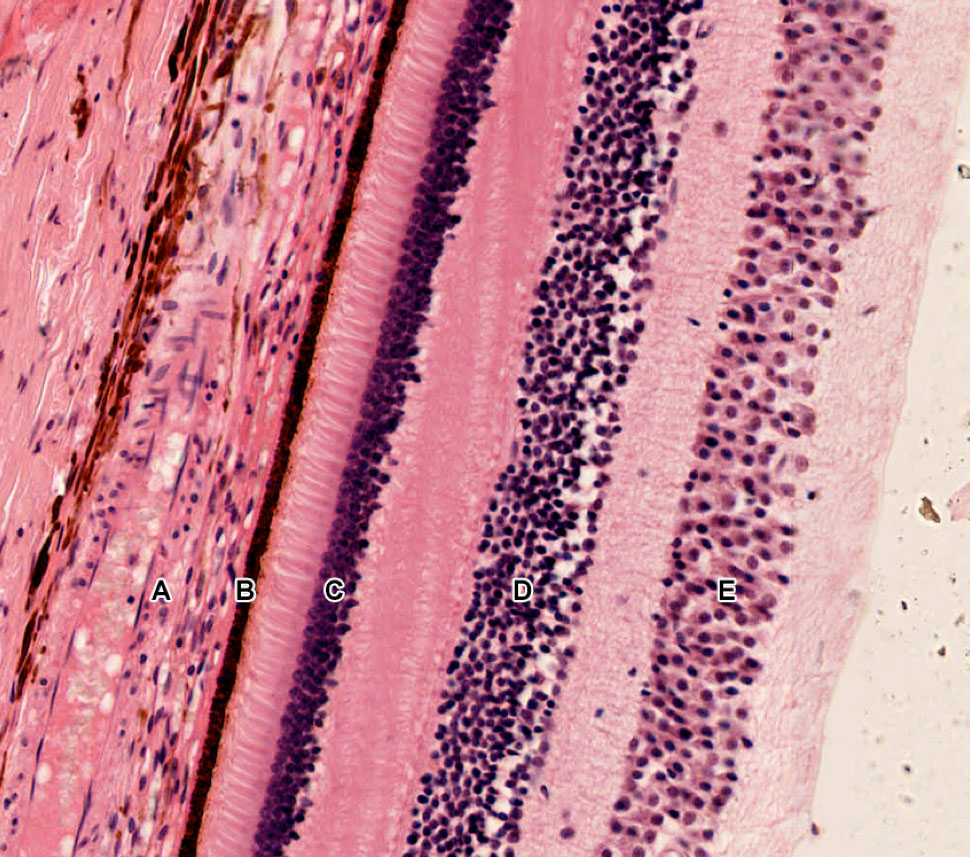
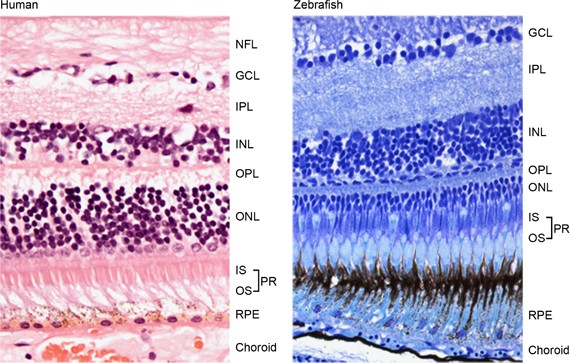
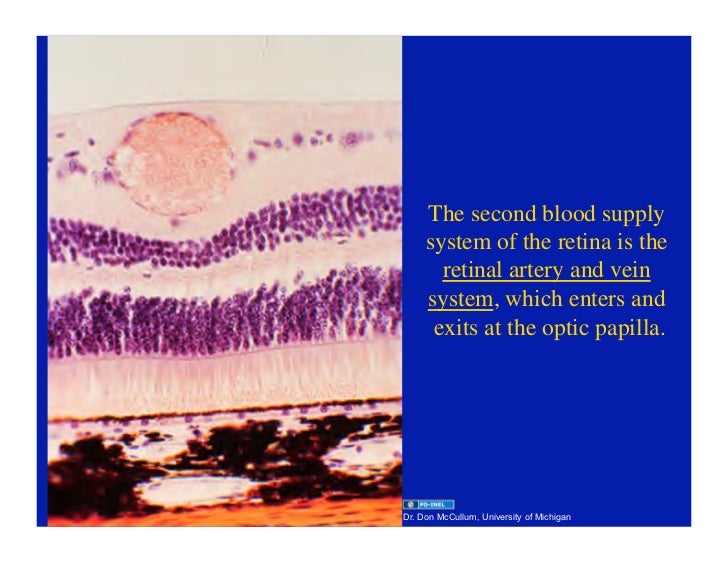
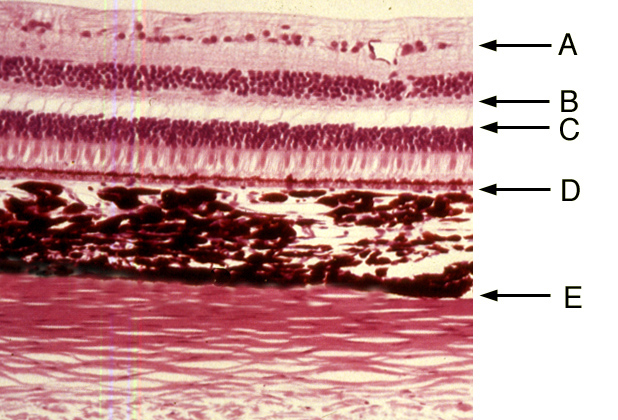
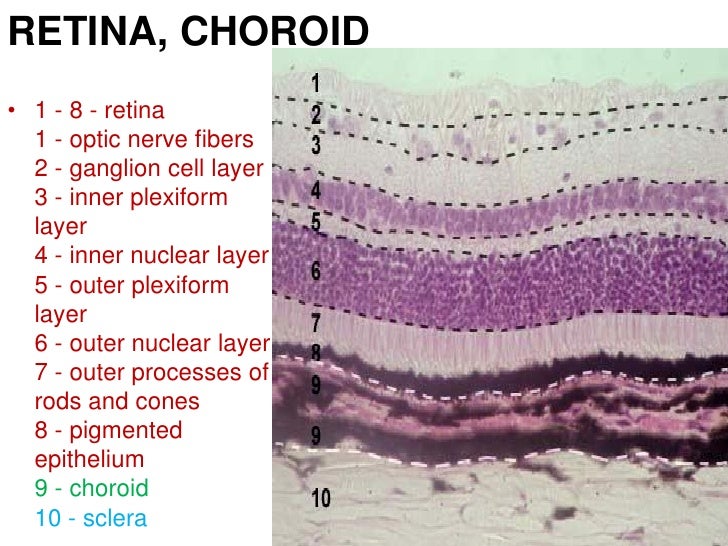
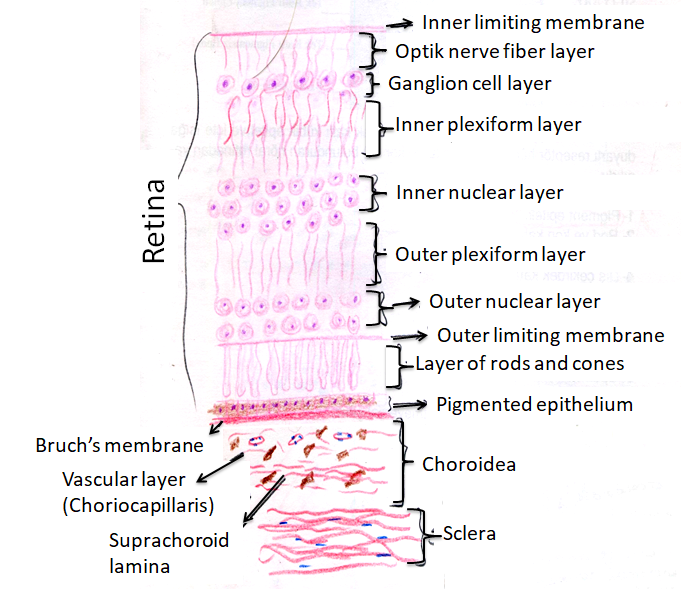
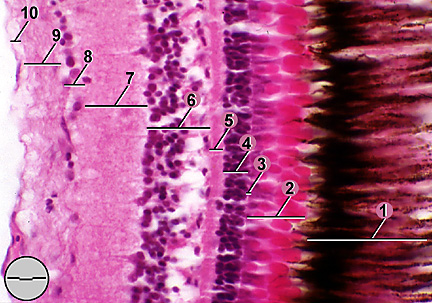
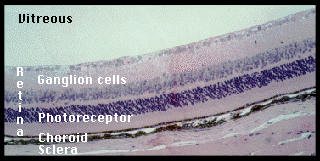
A histology b oct angiography octa. Multimodal imaging of macular circulation in a patient matched with postmortem examination of the same eye. Vestibular labyrinth and cochlear labyrinth slide ear 3 petrous temporal bone he embedded within the petrous portion of the temporal bone is the bony labyrinth which consists of the central vestibule three semicircular canals which arise and end at the vestibule and the cochleait contains a fluid called perilymph which has. The cellular layers of the retina are as follows.
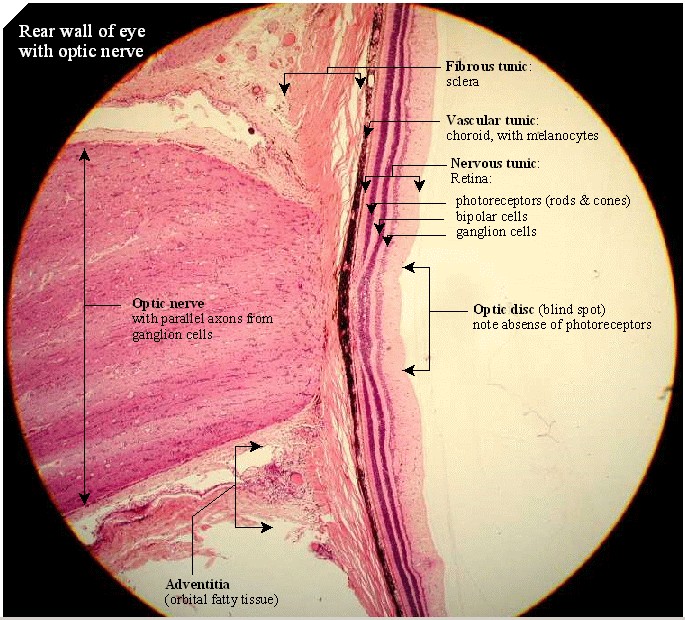
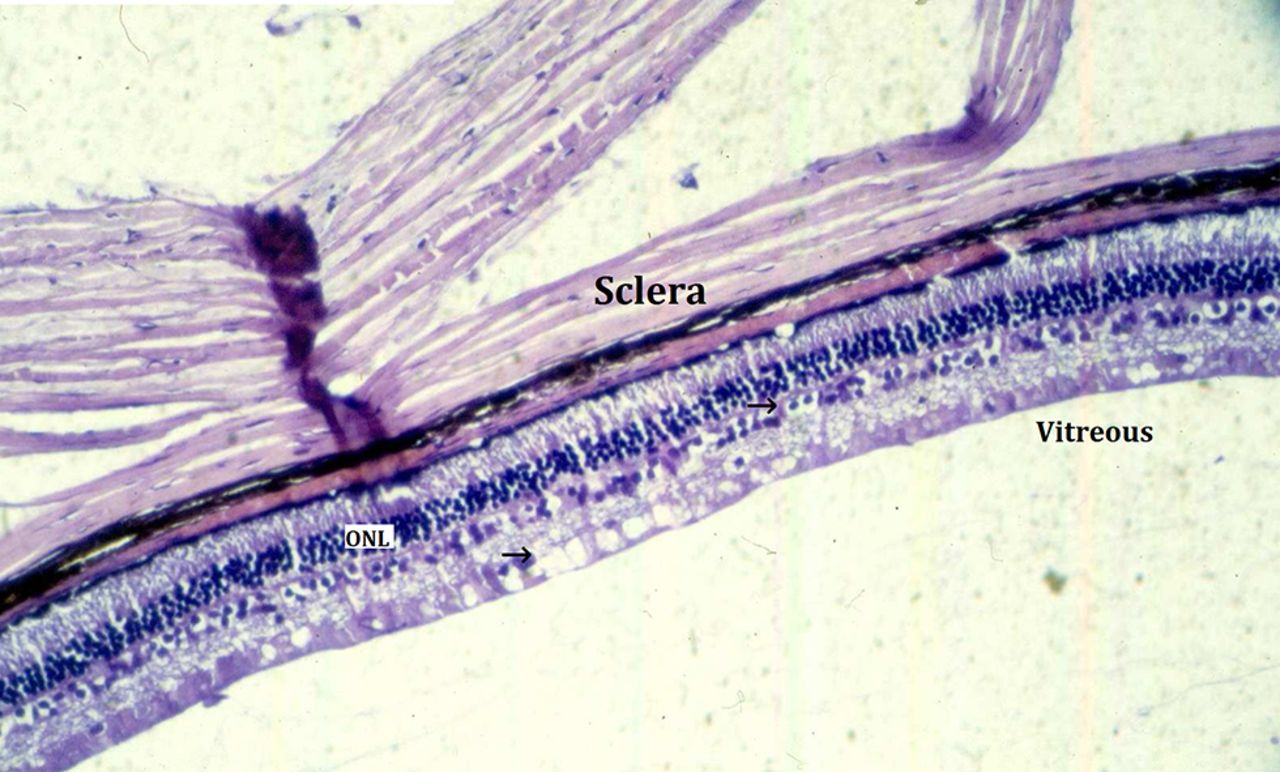
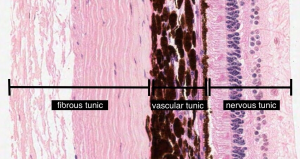
As a double layered epithelium the retina also covers the ciliary process and the posterior surface of the iris where it has both nutritive and structural functions. The retina is the innermost layer of the wall of the eye. From the center of the optic nerve radiates the major blood vessels of the retina. Farther back is the cell body which contains the cells organelles.
Learning objectives understand the structural organization and functions of the various components of the eyelid and conjunctiva. Name the three layers of the eye and describe the components of each at the level of the retina lens and iris and. The complexity of the retina from its precise multi layered structure to its various cell types and function will be discussed briefly in this overview.













:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11557/histology-retina-layerscells_english.jpg)